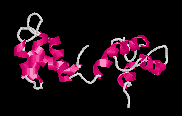
Ca2+-Free Calmodulin
Picture created with RasMac v2.6
PDB ID=1DMO |
Calmodulin
is an intracellular calcium receptor found ubiquitously
in eukaryotes. It is capable of regulating
biological activities of many cellular proteins
and transmembrane ion transporters mainly in a
Ca2+-dependent manner. When the
intracellular calcium level rises to 10-5
M, four Ca2+ ions bind to calmodulin,
and this Ca2+-calmodulin complex binds
the target proteins, initiating various signalling
cascades.
|
Calmodulin
has four EF-hand motifs that change conformation
upon binding calcium ions. Each EF-hand motif
contains two alpha helices connected by a 12-residue
loop. The calcium ion binds to the loop region
and changes the relative positions of the alpha
helices (Yap et
al, 1999). In absence of calcium, the alpha-helices
in the EF-hand motif of calmodulin are positioned
almost parallel to each other. This is known as
the closed conformation.
|
|
Upon
binding Ca2+, calmodulin undergoes
large conformational changes. The crystal structure
of Ca2+-loaded calmodulin exhibits
a dumbbell shape (Babu
et al., 1985, Babu
et al., 1988). However, it was later found
that part of the central linker region of Ca2+-bound
calmodulin is flexible in solution (Barbato
et al, 1992).
|
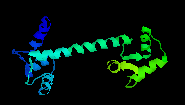
Ca2+-bound Calmodulin
Picture created with RasMac v2.6
PDB ID=3CLN |
Both
x-ray and NMR studies agree that the alpha helices
of the EF-hand motifs change their position relative
to each other, forming an almost perpendicular
conformation (open conformation). This radical
change allows calmodulin to increase its binding
affinity for a number of target proteins. Gerstein
and Krebs (1998) has a web
site with movies that illustrate how calmodulin
changes its conformation.
|
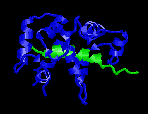
It
has been shown through numerous structural studies
that upon binding its target peptides, CaM forms
a compact globular conformation by bending its
central helix. Three calmodulin-binding peptides
that have been studied so far (skeletal
and smooth muscle myosin light chain kinases
and
calmodulin-dependent kinase II) form an alpha-helical
conformation which passes through the middle of
calmodulin, much like two hands holding onto a
rope.
|

|
Ca2+-bound
Calmodulinwith rabbit skMLCK
Picture created with RasMac v2.6
PDB ID=2BBM |
|
|
A
high content of methionine residues (9 out of 148 residues)
in calmodulin have been believed to be responsible for
the ability to bind numerous target proteins. Indeed,
8 of the 9 methionines are directly involved in binding
to all target peptides studied so far by x-ray and NMR.
On
this website, we present the IQ, 1-10, 1-14 and 1-16
motif classes and other motifs that have been identified
through sequence homology analyses by various investigators
and structural analyses that are available.
Please
browse through the website. There are programs that
predict whether a protein contains a calmodulin-binding
sequence (prediction
program), and calculate average hydrophobicity,
average hydrophobic moment and average propensity for
alpha-helix formation for a short peptide (analysis
program). You may also browse
the database that forms the basis of the prediction
program.
Note: If text or graphics do not display correctly,
try reloading the page.
|